Ever heard of ‘dimag ki rag phat jayegi’? Or someone saying, ‘sir dard se kanpati phat rahi hai’? That’s what an aneurysm pain feels like when it ruptures. But what is an aneurysm, and how do you know if you have one?
An aneurysm is a localized, abnormal bulging of a blood vessel wall, often caused by factors such as atherosclerosis, hypertension, genetic predisposition, trauma, or infection. They are commonly found in cerebral arteries, aorta, or peripheral vessels, aneurysms can pose serious health risks, particularly when they rupture, leading to life-threatening bleeding. The bad thing about aneurysm is symptoms are often absent until a rupture occurs, causing sudden and severe headaches, nausea, and loss of consciousness.
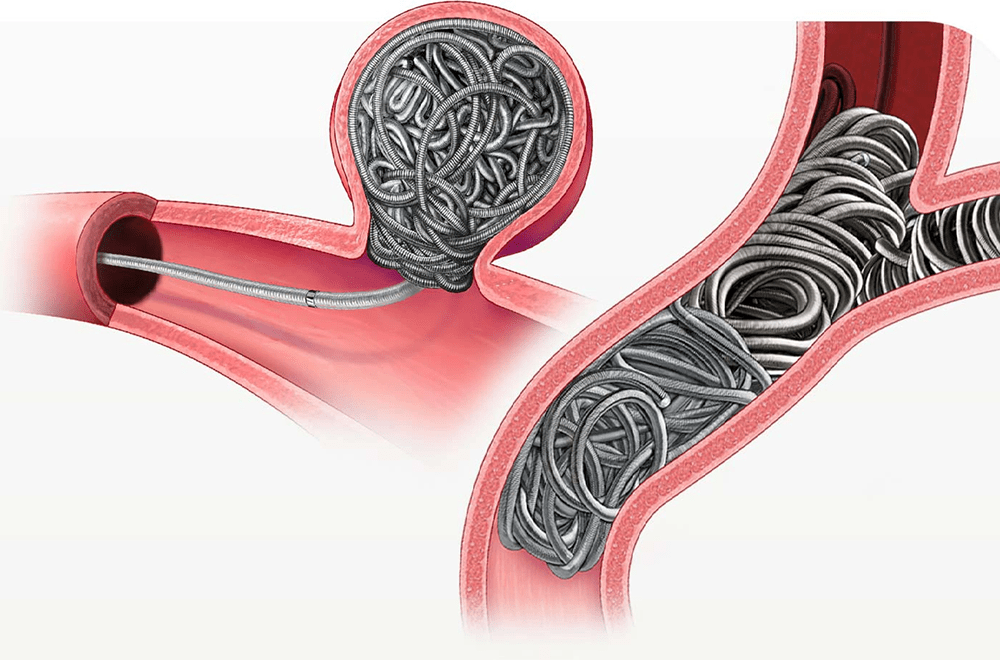
Treatment approaches vary and may involve monitoring, medication, or surgical interventions. Endovascular coiling procedures like coil embolization, which involves placing coils in the aneurysm to promote blood clot formation, is often employed.
Coil embolization procedure
Coil embolization, also known as endovascular coiling or coil occlusion, is a medical procedure used to treat certain vascular conditions, particularly those involving abnormal blood vessels. The most common application of coil embolization is in the treatment of cerebral aneurysms, but it can also be used in other parts of the body.
Patient Evaluation:
Imaging Studies: The process usually begins with diagnostic imaging studies, such as angiography or magnetic resonance angiography (MRA), to identify the location, size, and shape of the abnormal blood vessel or aneurysm.
Preparation:
Patient Preparation: The patient is typically placed under general anesthesia or conscious sedation, depending on the specific case.
Catheterization: A catheter is threaded through the blood vessels from a small incision, often in the groin, to reach the site of the abnormality.
Navigating to the Target Site:
Guidewire Placement: A guidewire is often used to help navigate the catheter through the blood vessels to the target location.
Contrast Dye: Contrast dye may be injected to enhance the visibility of blood vessels during the procedure.
Coil Deployment:
Coil Insertion: Once the catheter is in the correct position, small platinum coils (or sometimes other materials) are threaded through the catheter and released into the abnormal blood vessel.
Formation of Blood Clot: These coils promote the formation of a blood clot, which effectively seals off the abnormal blood vessel or aneurysm.
Post-procedure Evaluation:
Imaging Confirmation: After the coils are deployed, additional imaging studies are often performed to confirm that the coils are in the desired location and that blood flow to the abnormal vessel has been successfully blocked.
Recovery:
Postoperative Care: Patients are usually monitored in a recovery area for a certain period to ensure stability before being transferred to a regular hospital room.
Follow-up:
Long-term Monitoring: Patients who undergo coil embolization are typically monitored for the long term to assess the effectiveness of the treatment and to watch for any potential complications.
Benefits of embolization of aneurysm
Endovascular coiling offers several benefits as a minimally invasive treatment for aneurysm, especially cerebral aneurysms. Some of the key benefits include:
Minimally Invasive Procedure:
Unlike traditional open surgery, endovascular coiling is performed through small incisions using catheters and imaging guidance. This minimally invasive approach generally results in shorter recovery times, reduced pain, and a lower risk of complications associated with surgical incisions.
Reduced Recovery Time:
Patients undergoing endovascular coiling often experience a quicker recovery compared to those who undergo traditional open surgery. The shorter hospital stay and faster return to normal activities can contribute to an improved overall patient experience.
Preservation of Surrounding Tissues:
Since endovascular coiling is performed through blood vessels, it minimizes the need for large incisions and reduces the impact on surrounding tissues. This can be particularly important in delicate areas, such as the brain.
Decreased Infection Risk:
The risk of infection is generally lower with endovascular coiling compared to open surgery. The procedure is conducted in a sterile environment, and the small incisions reduce the exposure of internal tissues to external contaminants.
Avoidance of Craniotomy:
In the case of cerebral aneurysms, endovascular coiling can often be an alternative to a craniotomy (open surgery involving the removal of part of the skull). This can be especially beneficial for patients who may not be suitable candidates for open surgery due to their overall health or other medical conditions.
Quicker Return to Normal Activities:
Patients undergoing endovascular coiling may be able to return to their normal activities more quickly than those undergoing traditional surgery. This can contribute to a better quality of life for the patient.
Less Disruption to Blood Flow:
Endovascular coiling allows for precise placement of coils within the abnormal blood vessel, promoting the formation of a blood clot that blocks off the aneurysm. This targeted approach can be less disruptive to normal blood flow compared to open surgical techniques.
Effective Treatment:
Endovascular coiling has been shown to be an effective treatment for certain vascular conditions, particularly cerebral aneurysms. It can help prevent the risk of rupture and related complications.
What is considered a main benefit of endovascular coiling?
Endovascular coiling is a good way to treat aneurysms in the back part of the brain. About 8-15% of aneurysms are in this area, and they’re more likely to burst compared to those in the front part. Because these aneurysms are deep and near delicate structures like the brainstem, surgery is risky and can have a lot of problems.
Life expectancy after aneurysm coiling also increases. According to a study that surveyed 1003 people, more individuals were alive and independent in the group that underwent coil treatment compared to the neurosurgery group after 10 years. Additionally, the risk of rebleeding was very low in those who underwent coil embolization.
Dr. Imtiaz Ahmed is a highly experienced endovascular surgeon and interventional radiologist, renowned for pioneering minimally invasive surgery in Pakistan. One of his areas of expertise lies in performing coil embolization procedures with precision and skill. With his years of practice he has successfully helped many patients in preventing the occurrence of aneurysm rupture.
For further information email now at info@drimtiazahmad.com. Follow us on Instagram @Profdr_imtiaz_ahmad for daily updates.