What Are Cysts?
Ovarian cysts are fluid-filled sacs that develop inside or on the surface of the ovaries. Most ovarian cysts are harmless and form naturally during a woman’s menstrual cycle. In fact, many even disappear on their own. However, some may become large, burst, or twist, which requires quick medical care.
Common types of ovarian cysts include:
- Functional cysts: Appear during ovulation and often go away without treatment.
- Dermoid cysts: Contain tissue such as hair or skin and may grow over time.
- Endometriomas: Caused by endometriosis, when uterine tissue grows outside the uterus.
- Cystadenomas: Develop on the ovarian surface and can become quite large.
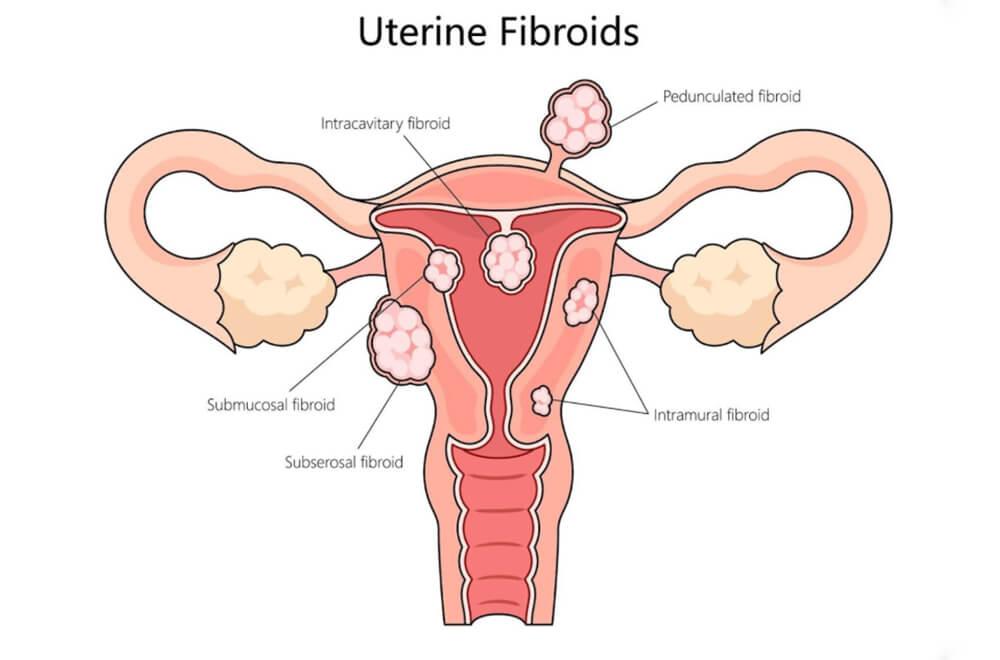
Uterine Fibroids vs Ovarian Cysts: Key Differences
Understanding the key differences between uterine fibroids and ovarian cysts helps with accurate and early diagnosis. Fibroids are solid and grow in the uterus, while cysts are fluid-filled and form on the ovaries. Additionally, fibroids grow slowly and rarely go away on their own. In contrast, most cysts form as part of the normal ovulation cycle and often shrink naturally.
Moreover, early symptoms and the regions of pain are also different for both of them. Fibroids cause heavy periods and pelvic pressure, but cysts tend to cause one-sided abdominal pain or bloating. Therefore, these patterns are essential to determine the difference between fibroids and cysts.
Symptoms of Fibroids and Cysts
Fibroids and cysts share some symptoms; however, there are key differences.
Common fibroid symptoms:
- Heavy or prolonged menstrual bleeding.
- Pelvic pressure or pain.
- Frequent urination.
- Constipation.
- Lower back or leg pain.
Common ovarian cyst symptoms:
- Sudden or dull pain on one side of the pelvis.
- Bloating or abdominal fullness.
- Pain during intercourse.
- Irregular periods.
- Nausea or vomiting, especially if the cyst ruptures.
For proper diagnosis, a pelvic ultrasound is the most reliable tool for confirming the difference between fibroids and cysts.
Causes of Fibroids
The exact cause of fibroids is still unknown, but several factors contribute. For instance:
- Hormones: Oestrogen and progesterone promote fibroid growth.
- Genetics: A family history raises the risk.
- Age: Most common between ages 30 and 50.
- Lifestyle: Obesity and high-fat diets may increase the chance of developing fibroids.
Causes of Ovarian Cysts
Ovarian cysts usually result from natural hormonal changes, but other causes include:
- Hormonal imbalance: Disrupted ovulation or fertility treatments.
- Pregnancy: Some cysts form early in pregnancy and may stay for months.
- Pelvic infections: Severe infections can spread to the ovaries.
- Endometriosis: Can cause endometriomas.
Hence, understanding uterine fibroids vs ovarian cysts key differences ensures accurate diagnosis and effective treatment.
Which Is More Dangerous – Cyst or Fibroid?
A common question often presented is, “Which is more dangerous cyst or fibroid?” In most cases, both are benign. However, cysts can become an emergency if they burst or twist, which may cause internal bleeding and sharp pain. On the other hand, fibroids rarely pose an immediate danger but can lead to heavy bleeding, anaemia, or fertility issues.
Therefore, the final decision to determine how dangerous the cyst or fibroid is made by doctors after considering the size, symptoms, and overall health of the patient.
Do Ovarian Cysts Affect Fertility?
A common question is, do ovarian cysts affect fertility? Most cysts, especially functional ones, do not. However, cysts linked to conditions like endometriosis or polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) can cause complications in conceiving.
Additionally, large or recurring cysts may harm ovarian tissue or disturb hormone levels. Therefore, when evaluating whether ovarian cysts affect fertility, doctors look at the cyst type and then present the final verdict.
What Size of Ovarian Cyst Is Dangerous?
Knowing what size of ovarian cyst is dangerous is vital for safe and early management. Often, small cysts under 5 cm go away naturally. Whereas cysts larger than 10 cm have a higher risk of twisting or bursting and may need surgery.
Thus, regular ultrasounds help track the cyst’s growth. Moreover, if pain worsens or the cyst persists, further evaluation is required to ensure timely treatment.
Diagnosis and Evaluation
To tell the difference between fibroids and cysts, doctors use several diagnostic methods, including:
- Pelvic exam: To detect masses or enlargement.
- Ultrasound: To identify whether the growth is solid or fluid-filled.
- MRI: To attain detailed images for treatment planning.
- Blood tests: To check for hormone levels and tumour markers.
Overall, accurate diagnosis allows healthcare providers to create a personalised treatment plan and avoid unnecessary interventions.
Treatment for Fibroids
Overall, the treatment depends on fibroid size, symptoms, and future pregnancy plans:
- Medication: Hormone therapy to reduce bleeding and shrink fibroids.
- Non-invasive treatment: MRI-guided ultrasound to destroy fibroids.
- Minimally invasive surgery: Uterine artery embolisation or myomectomy.
- Surgery: Hysterectomy for severe cases.
Furthermore, healthy habits, such as a balanced diet and regular exercise, may also help manage fibroid growth effectively.
Treatment for Ovarian Cysts
Primarily, the treatment for ovarian cysts varies depending on their size and type:
- Watchful waiting: Many cysts go away on their own.
- Surgery: Laparoscopy or open surgery for large or persistent cysts.
Most cysts usually resolve without treatment. Therefore, keeping a close check on the size of cysts is essential for proper management and tracking. Additionally, following up with regular ultrasounds ensures that any changes are identified early.
Prevention and Lifestyle Guidance
Although fibroids and cysts cannot always be prevented, adopting a healthy lifestyle can significantly lower the risk. To begin with, maintaining a nutritious diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains supports hormonal balance and overall wellness.
Additionally, staying active and keeping a healthy weight can help regulate hormone levels, which may reduce the chance of abnormal growths.
Furthermore, it is wise to limit caffeine and alcohol consumption, as excessive intake can influence hormonal activity. Likewise, managing stress effectively through mindfulness, relaxation techniques, or regular exercise plays an important role in reproductive health.
Most importantly, visiting your gynaecologist regularly ensures that any unusual changes are detected early.
Conclusion
In conclusion, knowing the difference between fibroids and cysts helps women take control of their reproductive health. While both are common and usually harmless, still early diagnosis and proper treatment are essential. Furthermore, by understanding the difference between fibroids and cysts, monitoring symptoms, and seeking timely medical help, complications can be avoided. Ultimately, staying informed and proactive ensures better health outcomes and peace of mind.